Insurance Regulatory Development Authority of India (IRDAI) has also identified a crucial link between the roles of KMPs and the excessive risk-associated to their position in Insurers, similar to the term of the private sector banks.
To address this, the IRDAI mandated the establishment of robust guidelines to have a Board-approved remuneration policy within the private insurers. This move aimed at mitigating risks arising from poorly aligned remuneration policies. Through these guidelines, IRDAI has linked Share-linked Instruments including Employee Stock Option Plan (ESOP’s) or a mix of cash and Share linked Instruments to the variable pay structure. Further the Cash linked stock appreciation rights (CSARs) are also to be treated as share linked instruments which will be tied to various performance parameters defined for the performance assessment of all KMPs.
To ensure that the goals of KMPs are in sync with the objectives of Insurers, IRDAI issued comprehensive guidelines on their remuneration structures. These guidelines referred as Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (Remuneration of Key Managerial Persons of Insurers) Guidelines, 2023 which provides a clear framework for Insurers and their Nomination and Remuneration Committees (NRCs) to craft effective remuneration policies.
Applicability of IRDAI’s Remuneration Guidelines for Private Sector Insurers:
These guidelines are applicable for all the Key Managerial Persons (KMPs) of private sector insurers, from financial year 2023-24.
IRDAI vide its Master circular on Corporate Governance for Insurers, 2024, has also clarified certain provisions in regard to the said Remuneration guidelines for KMP.
Key Highlights of remuneration guidelines;
- Performance parameters for performance assessment of KMPs.
- Balanced Components and Risk Alignment in compensation.
- Deferment of a portion of the variable pay.
- Malus and Clawback Provisions.
What is meant by the term “Share Linked Instruments”?
- Share-linked Instruments means (i) Employee Stock Option Schemes; (ii) Employee Stock Purchase Schemes; and (iii) Stock Appreciation Rights Schemes, for the purpose of these guidelines.
What is meant by the term “ESOPs”?
- Employee Stock Option Plan /Equity Incentive Plans (commonly referred to as ESOPs) give the employees an ownership interest by participating in the Stock /Shares of the Company.
- “Options/Units” is a right given to an Employee to purchase a given number of Shares of the Company at a future date, at a fixed pre- determined price.
Lifecycle of ESOP’s:
- Grant: The company grants options to employees.
- Acceptance: Employees accept the options.
- Vesting: Options vest with the employees.
- Exercise: Employees exercise options, paying the exercise price and applicable taxes.
- Allotment: Shares are allotted to employees.
- Sale: Employees sell their shares.
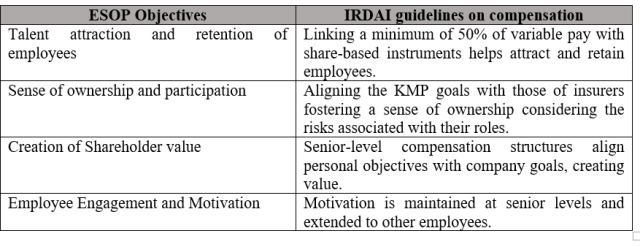
Alignment of ESOP objectives with IRDAI Compensation Guideline
Taxation Aspects of Share-linked Instruments:
“There is a double point at which taxation arises in the hands of employee”
- At Exercise: The difference between the market price and exercise price is added as a perquisite under salary.
- At Sale: Employees are liable for income tax on the sale of shares according to applicable laws
Thus, adapting and aligning the compensation structure is essential to maintain fairness and in the interest of the employees.
How can we assist you?
We offer advisory services for launching or aligning ESOP plans with RBI guidelines and other applicable norms. Our ESOP Management Tool, “ESOP Guardian,” can help automate the ESOP lifecycle. Contact us at mohini@indiacp.com or mahima@indiacp.com for assistance.
